Project funded by ANR/PRACE (2014-2018). Principal Investigator: Thierry Penduff
Most of the analyses of the OCCIPUT ensemble simulations have been performed in the framework of the PIRATE project
Ocean Chaos - Impacts, Structures, predicability
Characterizing the stochastic nature of the ocean variability on interannual-to-decadal timescales in a large ensemble of 1/4º ocean/sea-ice hindcasts.
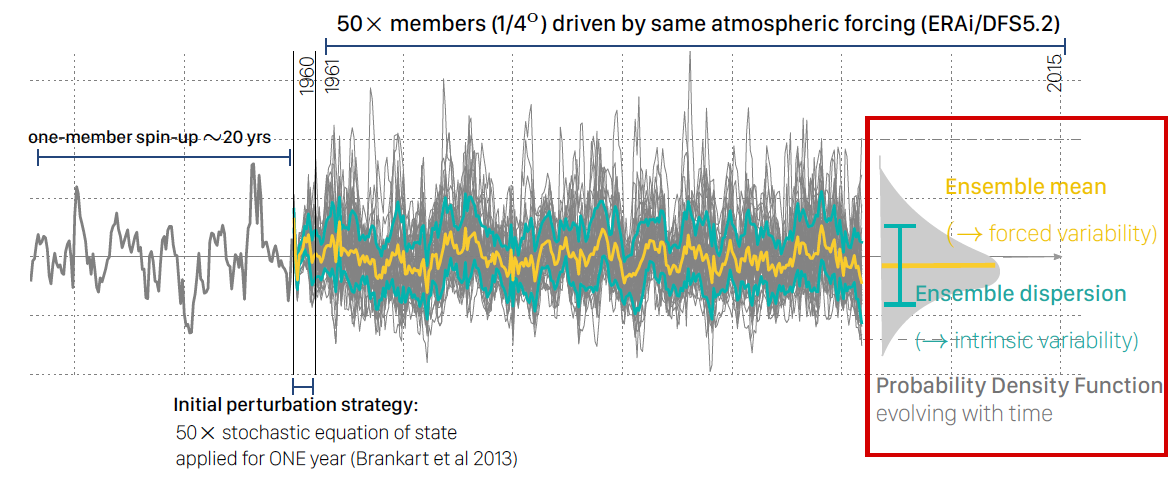
Turbulent ocean models spontaneously generate a chaotic variability up to multidecadal/basin scales. How this low-frequency chaos impacts climate-relevant oceanic indices is an important unsettled question. To separate this chaos from the atmospherically-forced response, MEOM and CERFACS have performed a pioneering 50-member ensemble of 1/4° global ocean/sea-ice simulations (1960-2015), starting from perturbed initial conditions then driven by the same atmospheric forcing with time. The results reveal the importance of the oceanic chaos up to large spatio-temporal scales and its modulation by the atmosphere, and this raises new issues about the detection/attribution of climate change in the ocean and the potential impact of this low-frequency chaos on the atmosphere.
.
Figure : The OCCIPUT ensemble experiment:
.
OCCIPUT documents and presentations:
-
OCCIPUT seminar given at Ecole de Physique des Houches, August 2017 [video]
-
OCCIPUT presentation given at the GMMC workshop, June 2016 [pdf] (10 Mo).
-
OCCIPUT ANR summary [here]
Publications related to OCCIPUT and PIRATE:
-
(2025) Börger, L., M. Schindelegger, M. Zhao, R. M. Ponte, A. Löcher, B. Uebbing, J.-M. Molines, T. Penduff, Earth System Dynamics, doi:10.5194/esd-2024-21, Chaotic oceanic excitation of low-frequency polar motion variability
-
(2024) Narinc, O., T. Penduff, G. Maze, S. Leroux, and J.-M. Molines, Ocean Science, https://doi.org/10.5194/egusphere-2024-1146 North Atlantic Subtropical Mode Water properties : Intrinsic and atmospherically-forced interannual variability
-
(2024) Sadhvi, K., I. Suresh, M. Lengaigne, T. Izumo, T. Penduff, J.-M. Molines, A.A. Can, and J. Vialard, Journal of Geophysical Research, https://doi.org/10.1029/2023JC020077 Intrinsic versus wind-forced Great Whirl non-seasonal variability
-
(2023) Zhao, M., R. M. Ponte, and T. Penduff, Science Advances, https://www.science.org/doi/epdf/10.1126/sciadv.adg0278 Global-scale random bottom pressure fluctuations from oceanic intrinsic variability
-
(2022) Hogg, A.McC., T. Penduff, S.E. Close, W.K. Dewar, N.C. Constantinou, and J.M. Martinez-Moreno, Journal of Geophysical Research, https://doi.org/10.1029/2022JC018440 Circumpolar variations in the chaotic nature of Southern Ocean eddy dynamics
-
(2022) Llovel, W., N. Kolodziejczyk, S. Close, T. Penduff, J.-M. Molines, and L. Terray, Environmental Research Letters, https://doi.org/10.1088/1748-9326/ac5f93 Intrinsic ocean variability in decadal regional sea level and ocean heat content trends using synthetic profiles.
-
(2021) Zhao, M., R. Ponte, T. Penduff, S. Close, W. Llovel, and J.M. Molines, Imprints of ocean chaotic intrinsic variability on bottom pressure and implications for data and model analyses. Geophysical Research Letters.
-
(2021) Fedele, G., T. Penduff, S. Pierini, M.C. Alvarez-Castro, A. Bellucci, and S. Masina, Climate Dynamics, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00382-021-05751-7 Interannual-to-decadal variability of the Kuroshio extension: Analyzing an ensemble of global hindcasts from a Dynamical System viewpoint
-
(2021) Carret, A., W. Llovel, T. Penduff, and J.-M. Molines, Journal of Geophysical Research - Oceans, https://doi.org/10.1029/2020JC017123, Atmospherically-forced and chaotic interannual variability of regional sea level and its components over 1993-2015
-
(2021) Cravatte, S., G. Sérazin, T. Penduff, and C. Menkes, Ocean Sci., 17, 487–507, https://doi.org/10.5194/os-17-487-2021, Imprint of chaotic ocean variability on transports in the Southwest Pacific at interannual timescales
-
(2020) Zhen, Y., P. Tandeo, S. Leroux, S. Metref, J. Le Sommer, and T. Penduff, J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 1–46, doi: 10.1175/JTECH-D-20-0001.1, An adaptive optimal interpolation based on analog forecasting: application to SSH in the Gulf of Mexico.
-
(2020) Close, S., T. Penduff, S. Speich, and J.-M. Molines, Progress in Oceanography, 184, doi: 10.1016/j.pocean.2020.102314, A means of estimating the intrinsic and atmospherically-forced contributions to sea surface height variability applied to altimetric observations .
-
(2019) Penduff, T., W. Llovel, S. Close, I. Garcia-Gomez, and S. Leroux, Surveys in Geophysics, doi: 10.1007/s10712-019-09571-7, Trends of Coastal Sea Level Between 1993 and 2015: Imprints of Atmospheric Forcing and Oceanic Chaos.. See the Link
-
(2018) Llovel, W., T. Penduff, B. Meyssignac, J.-M. Molines, L. Terray, L. Bessières, and B. Barnier, Geophysical Research Letters, 45, doi: 10.1029/2018GL080838, Contributions of atmospheric forcing and chaotic ocean variability to regional sea level trends over 1993–2015.
-
(2018) Zanna, L., J.M. Brankart, M. Huber, S. Leroux, T. Penduff, and P.D. Williams, Q. J. R. Meteorol. Soc. 2018;1–16; doi:10.1002/qj.3397, Uncertainty and Scale Interactions in Ocean Ensembles: From Seasonal Forecasts to Multi-Decadal Climate Predictions.
-
(2018) Penduff, T., G. Sérazin, S. Leroux, S. Close, J.-M. Molines, B. Barnier, L. Bessières, L. Terray, and G. Maze. Oceanography, 31(2). doi:10.5670/oceanog.2018.210. Chaotic variability of ocean heat content: Climate-relevant features and observational implications..
-
(2018) Leroux S., Penduff T., Bessières L., Brankart J.-M., Molines J.-M., Terray L., Barnier B., Serazin G., J. of Climate, 31(3) doi:JCLI-D-17-0168.1, Intrinsic and atmospherically-forced variability of the AMOC : insights from a large ensemble ocean hindcast.
-
(2017) Sérazin G., Jaymond A., Leroux, Penduff T., Bessières L., Brankart J.-M., Molines J.-M. , Terray L., Barnier B., Serazin G., Geophys. Res. Lett., 44(11):5580–5589, doi:10.1002/2017GL073026, (http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/2017GL073026) A probabilistic study of low-frequency ocean heat content variability: atmospheric influence versus oceanic chaos.
-
(2017) Bessières L., Leroux S., Brankart J.-M., Molines J.-M., Bouttier P.-A., Penduff T., Terray L., Barnier B., Serazin G., Geosci. Model Dev. Discuss., doi:10.5194/gmd-10-1091-2017, Development of a probabilistic ocean modelling system based on NEMO 3.5: application at eddying resolution.
-
(2014) T. Penduff, B. Barnier, L. Terray, G. Sérazin, S. Gregorio, J-M Brankart, M-P Moine, J-M Molines, P. Brasseur. CLIVAR Exchanges No. 65, Vol. 19, No. 2. Ensembles of eddying ocean simulations for climate.
-
(2016) Sérazin, G., B. Meyssignac, T. Penduff, L. Terray, B. Barnier, and J.-M. Molines, Geophys. Res. Lett., doi:10.1002/2016GL069273, Quantifying uncertainties on regional sea-level rise induced by multi-decadal oceanic intrinsic variability
-
(2015) Grégorio, S., T. Penduff, G. Sérazin, J.-M. Molines, B. Barnier, and J. Hirschi, J. Phys. Oceanogr., doi:10.1175/JPO-D-14-0163.1, Intrinsic variability of the Atlantic Meridional Overturning Circulation at interannual-to-multidecadal timescales
-
(2015) Sérazin, G., T. Penduff, S. Grégorio, B. Barnier, J.-M. Molines, and L. Terray, J. Climate, doi:10.1175/JCLI-D-14-00554.1, Intrinsic variability of sea-level from global 1/12° ocean simulations : spatio-temporal scales
Contact:
Thierry Penduff (P.I.).
Dataset:
The outputs of the OCCIPUT ensemble simulation are available upon request. Please contact Thierry Penduff (P.I.).
Project participants:
- MEOM/IGE, Grenoble, France.
- CERFACS, Toulouse, France.
